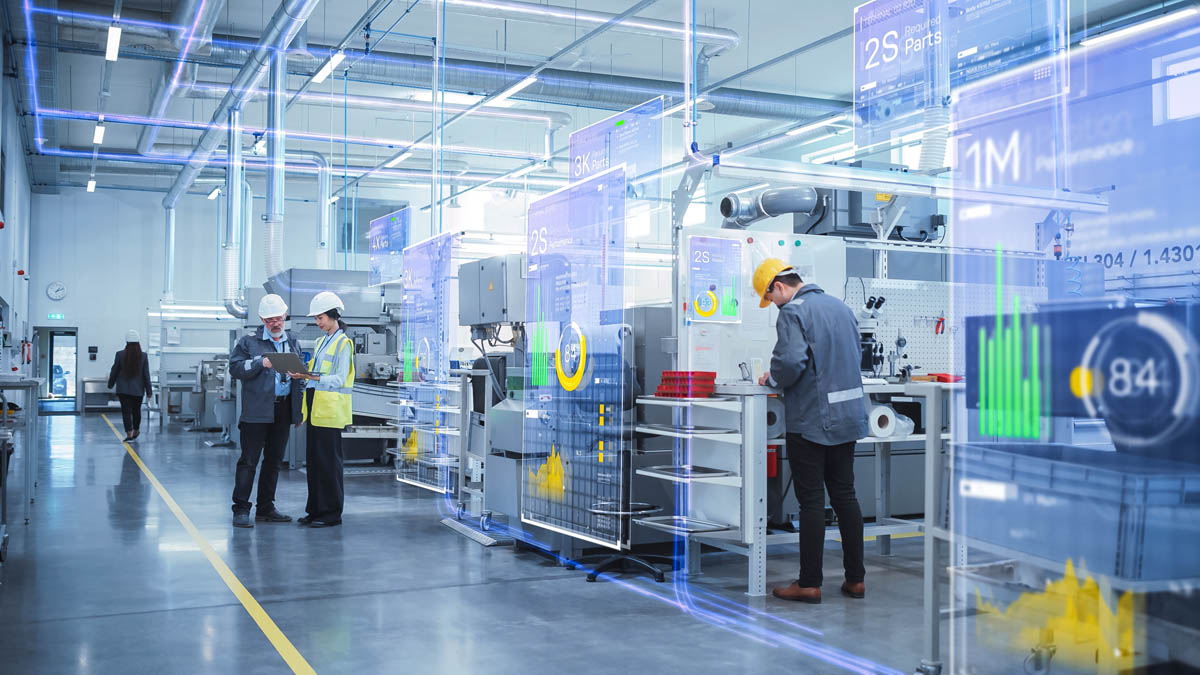
The evolution towards the Smart Factory must incorporate different types of industrial automation to enable companies that make up Industry 4.0 to improve processes, reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Explore with aggity the types of industrial automation crucial for a successful Smart Factory.
The Industrial automation is one of the essential components of the Industry 4.0. The so-called Smart Factory is employing an increasing number of technologies aimed at streamline processes, to improve efficiency and obtain a cost reduction. The use of control systems, the use of industrial sensors or the use of different machines for industrial robotics are just a few of the elements being used in smart factories, and all of this for several purposes: to improve production cycles, process quality and to achieve a more efficient production process. automated supply chain.
In industrial automation, however, different typologies come into play: they are not all the same and are not all used for the same purposes. Each Smart Factory uses different types depending on the sector in which it operates or the product line it works. Therefore, in the transition to the Smart Factory, it is important to choose the most suitable industrial automation technologies for the business. These are some of these technologies:
Fixed or rigid automation
This is a type of automation in which the automated machinery is designed to perform a specific task that is repetitive. In this case, it is difficult for these machines to perform any other task as they are highly specialized to operate in a specific environment and context. An example of this is an assembly line. The opposite case is flexible automation, where there can be reconfiguration of systems to perform different tasks and adjust to different situations.

Programmable automation
In this case we are talking about systems, equipment or robots that can be reprogrammed to perform different tasks. This type of automation is common in batch production, where tasks can change regularly, allowing for improved production efficiency. Another common example is a Computer Numerical Control (CNC) system, used in the manufacturing industry, which allows the production of high-precision parts without human intervention.
Adaptive automation
Similar to flexible automation, in this case automated systems are able to adapt and adjust in real time to changing environmental conditions. To do so, they often use advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) or Machine Learning to autonomously make decisions and carry out process optimization according to environmental conditions.
Robotic automation
Employed in a wide range of industries, from manufacturing processes to production lines to logistics, industrial robots are used to improve efficiency and productivity by performing repetitive and monotonous tasks quickly and accurately. In addition, these robots can work in environments that are dangerous or difficult for humans, which helps to improve plant safety.
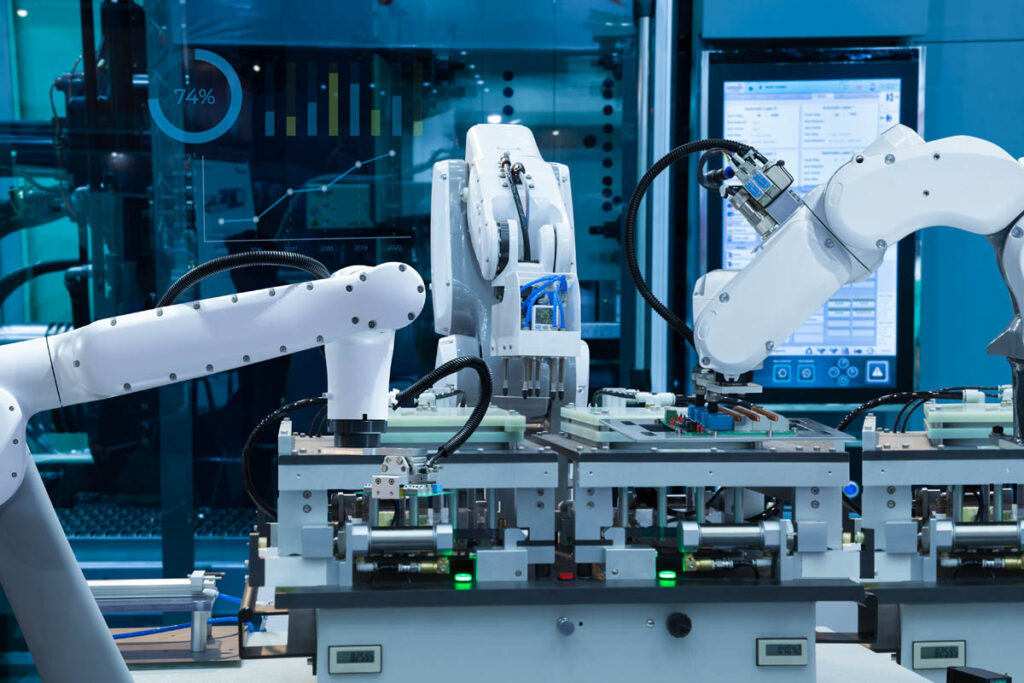
Process control automation
Incorporating production process control automation can bring a host of benefits, from reduced resource use to improved product quality. Its objective is to ensure optimal operation of industrial processes, while minimizing human error, maximizing efficiency, and improving the product quality. It is mainly used in the chemical and petrochemical industries.
Warehouse automation
As its name suggests, it is a technology that optimizes and speeds up storage and distribution operations in logistics centers. distribution in logistics centers. . This type of automation includes automated storage, conveying, sorting or management systems.
These are just some of the types of industrial automation in the Smart Factory, although there are many more. Despite all this, it is important to have a partner like aggity, an expert in helping Industry 4.0 companies implement a well-defined automation strategy. A solution such as Smart Factory by aggity comprehensively covers the management and control of production, quality, materials and maintenance activities.